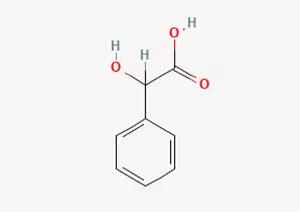
Dl-mandelic acid, also known as mandelic acid or α -hydroxyphenylacetic acid in the field of chemistry. Judging from its appearance, it presents as a pure white and flawless crystalline powder. Under specific temperature conditions, its melting point range is precisely defined between 118.0 and 121.0℃. It should be particularly noted that DL-mandelic acid has certain toxicity. When human skin comes into contact with it, it may trigger a series of adverse physiological reactions. And if it is accidentally ingested, it will cause serious harm to physical health.
However, unexpectedly, DL-mandelic acid, due to its powerful antibacterial effect, can be directly taken orally to treat urinary tract infections in certain specific circumstances, which to a certain extent reflects its unique value in the field of medicine.
It is worth mentioning that DL-mandelic acid has the special structural feature of chiral molecules, which enables it to play a crucial role in many fields and has already become an important chiral drug intermediate and fine chemical product. Its application value is very extensive. It can not only be ingeniously used in the synthesis of various drugs, such as the vasodilator cyclomannitate, which has a significant effect on improving the vascular-related functions of the human body; There is also the anti-inflammatory drug DL-hexamethylenetetramine mandelate specifically used for the treatment of urinary tract infections, which can play an important role in dealing with urinary tract infections. And antispasmodic drugs such as DL-benzyl mandelate have made significant contributions in alleviating spasmodic symptoms. Moreover, DL-mandelic acid also has the dual effects of a spermicide and trichomonas, and has corresponding applications in some specific scenarios.
From the perspective of market consumption, as early as 2012, the consumption of DL-mandelic acid in China reached approximately 250 tons. Furthermore, in terms of the current international market situation, the demand for DL-mandelic acid is in a stage of steady increase and is continuously growing at an average annual rate of about 10%. This fully demonstrates its high demand and broad development prospects in the international market.
Tracing back to the origin of mandelic acid, it was carefully extracted from peach leaves and willow leaves at the very beginning. It belongs to a lipophilic fruit acid and has the remarkable characteristics of high affinity with the skin and strong permeability. Compared with glycolic acid, its nature is milder. Because its chemical structure is similar to that of antibiotics, it can effectively inhibit the proliferation of many bacteria.
It is precisely because of its excellent lipophilicity and antibacterial properties that mandelic acid has also demonstrated unique advantages in skin care and other fields. It can precisely inhibit Propionibacterium acnes and at the same time improve the blockage of hair follicle sebaceous gland ducts. Not only that, mandelic acid also has a significant effect on improving pigmentation problems left over from photoaging and inflammation. In the actual clinical practice process, the combination of salicylic acid and mandelic acid has been widely used in skin peeling treatment, providing an effective treatment plan for solving many skin problems.