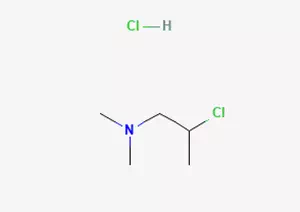
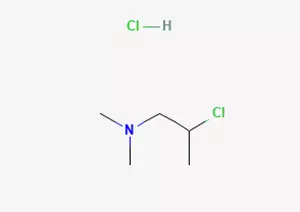
In the field of organic chemistry synthesis, there is an important compound preparation process, that is, 2-dimethylamino-2-propanol is chlorinated with thionyl chloride through a specific chemical reaction to obtain 2-dimethylamino-isopropyl chloride hydrochloride.
Specifically, under suitable reaction conditions, 1-dimethylamino-2-propanol was reacted with thionyl chloride. Through a series of complex chemical change processes, 2-dimethylamino-isopropyl chloride hydrochloride was finally successfully prepared. This compound has some remarkable characteristics in terms of chemical properties.
Among them, 2-dimethylaminoisopropyl chloride is incompatible with solid oxidants. This is because its chemical structure determines that when it encounters solid oxidants, it may undergo intense chemical reactions, thereby affecting the stability and safety of the substance.
From the perspective of chemical classification, amines belong to a type of chemical base. Amine compounds have unique chemical properties and can undergo neutralization reactions with acids. During the neutralization reaction, amines interact with acids to form corresponding salts and water. Moreover, these acid-base reactions are exothermic, which means that a certain amount of heat is released during the reaction process. It is worth noting that during the neutralization process, the heat released per mole of amine is largely not directly related to the toughness of the amine itself as a base.
In addition, amines may also be incompatible with many other substances. For instance, amines may react with isocyanates. When the two meet, a series of chemical changes may be triggered, leading to alterations in the properties of the substances. Amines and halogenated organic compounds may also be incompatible, and complex interactions may occur between them. Peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides and acyl halides and other substances may also react with amines, thereby affecting the stability and application effect of amines.
Under certain specific chemical reaction conditions, when amines combine with strong reducing substances (such as hydrides), flammable gas hydrogen is produced. This reaction not only alters the composition and properties of substances, but may also bring certain safety risks, as hydrogen is a flammable and explosive gas.
Regarding the flash point data of 2-dimethylaminoisopropyl chloride, there is no clear record at present. However, based on its chemical structure and related properties, it is speculated that 2-dimethylaminoisopropyl chloride may be flammable. This means that when storing, using and handling this compound, special attention should be paid to safety measures such as fire prevention and explosion prevention to prevent accidents.