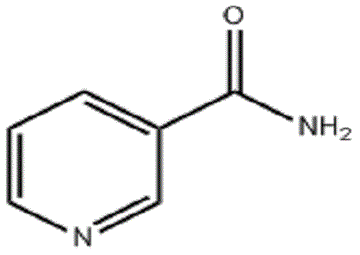
English Synonyms
NicotinamideForBiochemistry;NicotinamideB.P.,U.S.P.;Niacinamide/Nicotinamide;Nicotinamide(Niacinamide)Nicotinamide(Niacinamide)Bp/Usp;Nicotinamide,98%;Vitamin B3;Nicotinamidum;NIACINAMIDE USP GRANULAR
Niacinamide Properties
| Melting Point | 128-131 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling Point | 150-160 °C |
| Density | 1.40 |
| Vapor Density | 4.22 (vs air) |
| Vapor Pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| Refractive Index | 1.4660 (estimate) |
| Flash Point | 182 °C |
| Storage Conditions | 2-8°C |
| Solubility | 691g/l |
| Acidity Coefficient (pKa) | 3.3(at 20℃) |
| Form | Powder |
| Color | White |
| PH | 6.0-7.5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | 1000 g/L (20 ºC) |
Decomposition
| >=200 °C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with Strong Oxidizing Agents. |
Uses and Synthesis of Nicotinamide
Introduction
Nicotinamide, Also Known as Nicotinamide, Vitamin B3 or Vitamin Pp, Is a Water-Soluble Vitamin Belonging to the B Vitamins. It Is a Component of Coenzyme I (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, Nad) and Coenzyme Ii (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate, Nadp). The Nicotinamide Part of the Two Coenzyme Structures in the Human Body Has Reversible Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation Properties, Plays a Role in Hydrogen Transfer in Biological Oxidation, Can Promote Tissue Respiration, Biological Oxidation Process and Metabolism, And Is of Great Significance to Maintaining the Integrity of Normal Tissues, Especially the Skin, Digestive Tract and Nervous System. When It Is Deficient, Pellagra Is Caused Due to the Impact on Cell Respiration and Metabolism, So This Product Is Mainly Used to Prevent and Treat Pellagra, Stomatitis, Glossitis, Etc.
Chemical Properties
Nicotinamide Is a White Needle-Shaped Crystal or Crystalline Powder, Odorless or Slightly Odorous, Slightly Bitter. Relative Density 1.4, Melting Point 129-131℃. 1g of This Product Can Be Dissolved in 1ml Water, 1.5ml Ethanol or 10ml Glycerol, Insoluble in Ether. The Ph of a 10% Aqueous Solution Is 6.5-7.5. It Has Weak Hygroscopicity. It Is Relatively Stable, Resistant to Acid, Alkali and High Temperature. It Is Stable to Light and Heat in Dry Air. It Generates Nicotinic Acid When Heated in Alkaline or Acidic Solutions. The Oral Ld50 of Rats Is 2.5-3.5g/Kg, And the Adi Value Is Not Specially Specified (Ecc, 1990).
Food Sources
In Nature, It Mainly Exists in the Outer Skin of Cereals, Yeast, Peanuts, Meat, Animal Organs, Milk and Green Leafy Vegetables. It Can Be Synthesized from Tryptophan in the Human Body, But the Efficiency Is Extremely Low. Escherichia Coli and Other Bacteria in the Intestines Can Synthesize Niacin and Then Convert It into Niacinamide.
Application
Nicotinamide and Niacin Are Commonly Used in Most Conditions. Nicotinic Acid Also Generates Niacinamide in Animals. When the Body Lacks Niacin and Niacinamide, Pellagra Will Occur. Therefore, They Can Prevent Pellagra. They Play a Role in the Metabolism of Proteins and Sugars and Can Improve the Nutrition of Humans and Animals. In Addition to Being Used as Medicine, They Are Also Used in Large Quantities as Food and Feed Additives. The Global Production Capacity Has Exceeded 30,000 Tons. In Japan, 40% of Niacinamide Is Used in Medicine, 50% as a Feed Additive, And 10% as a Food Additive. Nicotinic Acid and Niacinamide Are Non-toxic and Are Mostly Found in Animal Liver, Kidney, Yeast and Rice Sugar in Nature. The Ld50 of Niacinamide for Subcutaneous Injection in Rats Is 1.7 Grams/Kilogram.
Whitening Principle
There Are Two Main Whitening Principles of Niacinamide: First, Niacinamide Can Interfere with the Transport of Melanin, Confining Melanin in Melanocytes, Preventing Melanocytes from Continuing to Produce Melanin, And at the Same Time Preventing Melanin from Being Transferred to the Skin Surface to Darken the Skin, Thereby Achieving a Whitening Effect. Second, Niacinamide Has Been Proven to Have a Good Anti-Glycation Effect, And the Substance Produced by Skin Glycation Is Brown, Which Makes the Skin Look Darker. Niacinamide's Anti-Glycation Helps Whiten the Skin and Brighten the Skin Tone.
Effects
Moisturizing, oil control, and reducing blackheads Niacinamide can effectively reduce transepidermal water loss. Although the effect is not as good as hyaluronic acid and glycerin when used alone, the effect of using them together is definitely 1+1>2; Niacinamide can calm the sebaceous glands that are in an "excited" state, thereby achieving the effect of controlling oil and reducing blackheads and acne.
Good anti-wrinkle ability: Niacinamide's anti-wrinkle ability lies in its ability to activate ATP, provide vitality to keratinocytes, increase collagen synthesis, and has good synergistic ability, and can be used together with other anti-wrinkle ingredients.
Very good auxiliary sunscreen effect. The harm caused by ultraviolet rays to the human body is not only tanning, but also immunosuppression and even skin cancer. Many studies at home and abroad have shown that niacinamide can effectively reduce the occurrence of skin photoimmunosuppression when exposed to ultraviolet rays.
Good mildness Compared with vitamin C, resorcinol derivatives and other ingredients, niacinamide is quite mild and can be used by most people. However, you still need to pay attention to the skin tolerance. For example, the 10% niacinamide concentration of The Ordinary whitening essence is still irritating. Therefore, it is best to undergo a skin tolerance test before use to confirm tolerance. At the same time, be careful not to use it together with acid-containing products, such as salicylic acid and fruit acid, to prevent excessive irritation to the skin.
Metabolism and Absorption
Nicotinamide is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract when taken orally, and is absorbed faster when injected intramuscularly. After absorption, it is distributed to all tissues of the body, with a t1/2 of 45 minutes. It is metabolized by the liver, and most of it is metabolized into N-methylnicotinamide. Only a small amount of the therapeutic dose is excreted in the urine in its original form. When the dose exceeds the need, the excretion increases. If the daily urine N-methylnicotinamide is less than 4mg, it indicates a deficiency of nicotinamide.
Adverse Reactions
Occasionally, dizziness, nausea, upper abdominal discomfort, loss of appetite, etc. may disappear on their own. Excessive use in early pregnancy may cause teratogenicity. Intramuscular injection may cause pain, so it is used sparingly.
Production Method
Nicotinic acid, boric acid and ammonia water are put into a reaction pot, ammonia is introduced under stirring, and the temperature is raised to dissolve; then ammonia is distilled to recover, and after reaching 120°C, it is transferred to a dehydration pot for further concentration; when the temperature reaches 145°C, liquid ammonia is added, and the reaction is continued at 185-190°C for 20-30 hours. Then the temperature is lowered to 130°C, dilute with distilled water, activated carbon is added, and ammonia is introduced for decolorization at 70-80°C for 2 hours; after the reaction, it is filtered while hot, the filtrate is cooled in water for 24 hours, separated and crystallized, and washed with ethanol and dried to obtain the finished product with a yield of 89%.