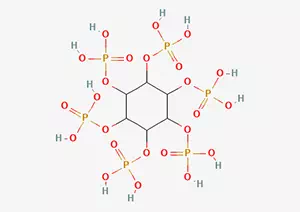
What is Phytic acid CAS 83-86-3?
Physical properties
Density: 2.42 g/cm³
Boiling point: 105°C (atmospheric pressure)
Solubility
Readily soluble in water, ethanol and acetone;
Insoluble in anhydrous ethanol, ether, benzene and chloroform.
Stability: The aqueous solution is prone to decomposition at high temperatures and needs to be stored at low temperatures.
Chemical properties
Strong acidity: Low pH value, with strong chelating ability, it can form insoluble salts with metal ions (Ca²⁺, Fe²⁺, Mg²⁺, Zn²⁺).
Interaction with proteins: It forms complexes with proteins at specific pH values, affecting digestion and absorption
Phytic acid CAS 83-86-3 Use
Food industry: Antioxidants, preservatives (fruits, vegetables, aquatic products), color protectants, deodorants inhibit oxidation, extend shelf life, and stabilize color
Medicine and daily chemicals: Raw material for inositol production, anti-swelling agent for toothpaste, whitening agent for cosmetics, chelating metal detoxifier for heavy metals, inhibition of tyrosinase, anti-caries
Industry and chemical engineering: Metal rust inhibitors, electroplating brighteners, PVC polymer anti-sticking agents, textile antistatic agents form protective films, disperse particles, flame retardants
Environmental protection and materials: Water softeners, rare metal enrichment agents, plastic flame retardant modifiers, chelating ions, catalytic reactions
Phytic acid CAS 83-86-3 safety
Acute toxicity (oral) :
Mouse LC₅₀ : 500 mg/kg
Rabbit LDLo: 45 mg/kg
Mouse LC₅₀ : 4192 mg/kg (50% solution).
Security:
It is a low-toxicity substance (oral LD₅₀ in mice is approximately 4.9 g/kg, which is lower than lactic acid);
Excessive intake may interfere with the absorption of minerals such as calcium and iron.
Service
* Prompt reply and 24 hours online, professional team to provide best price and high quality product.
* Sample testing support.
* Every batch of products will be tested to ensureits quality.
*The packing also can be according the customers` requirment.
*Any inquiries will be replied within 24 hours.
*we provide Commerical Invoice, Packing List, Bill of loading, COA , Health certificate and Origin certificate. If your markets have any special requirements, let us know.