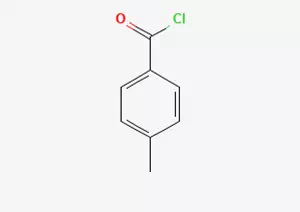
In the vast field of chemistry, p-toluene chlorine, as a specific chemical substance, has its unique and clear chemical identity. Its molecular formula was precisely determined as C8H7ClO. This concise yet crucial chemical formula, like the "ID card" of the substance, clearly reveals the composition mystery of its molecular structure. After precise calculation and determination, its molecular weight was identified as 154.5936. This specific value reflects its mass characteristics in the microscopic world.
From the appearance, p-toluene chlorine presents in the form of white crystalline powder. These tiny crystal particles, like countless fine snowflakes, are pure and uniform, presenting a simple and stable material form on a macroscopic scale.
When we further explore the physical properties of p-toluene chlorine, we will find a series of precise and meaningful data. Its density is 1.16. This value indicates the mass characteristics of the substance within a certain volume, reflecting the tightness of the arrangement between its molecules and the fullness of the substance. The melting point is -2℃. At this specific temperature, p-toluene chlorine begins to change from a solid state to a liquid state. This process marks a significant shift in its molecular motion state and also provides us with important reference information about the changes in its material state. The boiling point is between 225 and 227℃. When the temperature reaches this range, the liquid p-toluene chlorine will vaporize rapidly. This property is of great significance in many chemical processes and experimental operations. The refractive index is between 1.5525 and 1.5545. This optical property enables p-toluene chloride to exhibit unique refraction behavior during the propagation of light, and also provides a basis for related optical analysis and applications. In addition, its flash point is 82℃, which means that under specific conditions, p-toluene chlorine has a distinct flammability characteristic. Therefore, we need to pay extra attention to safety precautions during actual operation and use.
On the broad stage of the chemical industry, p-toluene chlorine plays an important role. It is often used as an intermediate in fields such as medicine, pesticides, photosensitive materials and dyes. In the field of medicine, it is a key precursor for synthesizing numerous complex drug molecules. Through a series of sophisticated chemical reactions, compounds with specific pharmacological activities can be constructed. In terms of pesticides, p-toluene chlorine is involved, providing an important basis for the development of highly efficient and low-toxicity pesticide products. For photosensitive materials, it is one of the key components for achieving photosensitive properties, facilitating the development of photosensitive materials with excellent performance. In the dye industry, p-toluene chlorine is also an indispensable part, contributing its own strength to the colorful dye world.
So, how is such an important chemical substance prepared? Generally speaking, p-toluene chlorine can be produced by the reaction of pre-treated p-toluene acid material with thionyl chloride. During this process, the p-toluenic acid material undergoes meticulous pretreatment to endow it with appropriate reactivity and purity, and then undergoes a chemical reaction with thionyl chloride to generate p-toluenic chloride.
However, it should be noted that in the general preparation process of p-toluene chloride, the generation of p-chloromethylbenzoyl chloride, a genotoxic impurity, is often accompanied. In the crucial step of the chlorination reaction, due to the complexity of the reaction conditions and the characteristics of the chemical reaction, p-chloromethylbenzoyl chloride will react with other reagents, thereby generating genotoxic impurities. The presence of such impurities undoubtedly brings potential risks and challenges to the application of toluene chlorine.
For this reason, in the process of preparing and applying p-toluene chlorine, it is particularly important to strictly control its content. After unremitting efforts and exploration, the scientific researchers successfully obtained the target substances of excellent quality by adopting the preparation methods reported in the literature. Under this optimized preparation method, the content of chloromethylbenzoyl chloride can be effectively controlled, keeping it within 100PPM. In the optimal case, its content can even be controlled within 10PPM. Meanwhile, the content of other impurities can also be strictly controlled within 0.02%, ensuring the purity and safety of p-toluene chlorine and providing a solid guarantee for its wide application in various fields.