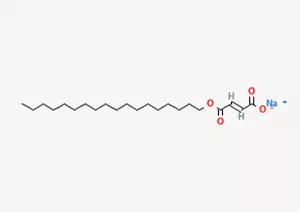
Sodium Stearyl Fumarate Uses
In today's pharmaceutical and food industries, sodium stearoyl fumarate (C22H39NaO4) is undoubtedly a widely used and crucial excipient. It plays an indispensable role in many fields. Its unique chemical properties and excellent application effects make it an indispensable part of the pharmaceutical and food industries.
The metabolic process of sodium stearoyl fumarate in animals is a complex yet orderly one. When it enters the animal's body, most of it will be absorbed and hydrolyzed through a series of physiological reactions. During this process, it will gradually decompose to form stearol and stearic acid. These two substances have their own metabolic pathways and functions in the animal body. A small portion of sodium stearyl fumarate can be metabolized directly and rapidly. It is worth noting that this substance does not produce any toxic substances during the metabolic process and does not cause any irritation to the animal body. This undoubtedly provides a strong guarantee for its safe application in the fields of medicine and food.
In the field of pharmaceuticals, the application of sodium stearyl fumarate is extremely extensive and crucial. During the production process of drug preparations, it is often carefully added to various drug preparations and plays multiple important functions. For instance, it can be used as an efficient lubricant and is widely applied in the production process of tablets and capsules. During the tablet pressing process, sodium stearoyl fumarate can form a uniform lubricating film between the mold and the drug powder, effectively reducing the friction between the drug particles and the mold, making the tablet pressing process smoother and thereby improving the quality of the tablets and production efficiency. For capsules, it can also play a lubricating role, ensuring the smooth filling and sealing process of the capsules and avoiding problems such as cracking or deformation during the production process.
In addition, sodium stearyl fumarate plays a unique role in the production of effervescent tablets. It can form a protective film on the surface of the effervescent tablet. This protective film is like a solid barrier and can effectively solve some problems that may occur during the use of stearic acid-based lubricants. For instance, stearic acid-based lubricants may cause instability of drug components or affect the disintegration rate of drugs in some cases, while the protective film formed by sodium stearyl fumarate can prevent these problems from occurring. Meanwhile, this protective film can also improve the disintegration performance of the drug, enabling it to disintegrate more quickly when exposed to moisture or other solvents, thereby promoting the dissolution of the drug, enhancing its bioavailability, and allowing the drug to better exert its therapeutic effect.
In the field of food, sodium stearyl fumarate also holds an important position. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) explicitly allows sodium stearyl fumarate to be directly added to food consumed by humans as a regulator and stabilizer. This regulation fully demonstrates its safety and reliability. In actual food production, sodium stearyl fumarate is widely used in the manufacturing processes of various baked goods, flour thickening foods, dried potatoes, and processed grains, among others.
Take baked goods as an example. When making bread, biscuits and other baked goods, sodium stearyl fumarate can be used as a regulator to help adjust the structure and texture of the dough, so that the baked goods have a better taste and appearance. In flour-based thickened foods, it can act as a stabilizer, preventing phenomena such as stratification and sedimentation during storage and transportation, and extending the shelf life of the food. For foods such as dried potatoes and processed grains, the addition of sodium stearyl fumarate can also improve the quality and taste of the food, making it more in line with consumers' taste demands.
Moreover, there are clear regulations on the addition amount of sodium stearyl fumarate in food. The addition amount can account for 0.2% to 1.0% of the food weight. This strict addition amount range has been verified through extensive scientific research and practice. It can not only ensure that sodium stearoyl fumarate plays the best regulatory and stabilizing role in food, but also guarantee the safety and health of food, allowing consumers to consume food containing sodium stearoyl fumarate with confidence.